Full text loading...
There is considerable interest in the occurrence and molecular mechanisms of phenotypic plasticity and genotype-by-environment interactions (G×E) in plant populations. The emergence of genomic tools, including quantitative trait locus (QTL) mapping and transcriptome studies, provides opportunities to identify G×E patterns and mechanisms across a diversity of phenotypes, species, and environments. We review progress in evaluating the presence and characterizing the mechanisms of G×E using genomic studies of abiotic responses in plants. Our review reveals that G×E is common, often caused by changes in the magnitude of genetic effects in response to the environment, and associated with diverse genetic factors and molecular variants. We illustrate this diversity with an examination of transcriptome studies and discussion of cloned genes underlying G×E. We discuss the caveats associated with existing studies and outline future directions for better understanding G×E and its impact on local adaptation and plant improvement.

Article metrics loading...

Full text loading...


Data & Media loading...
Supplemental Material
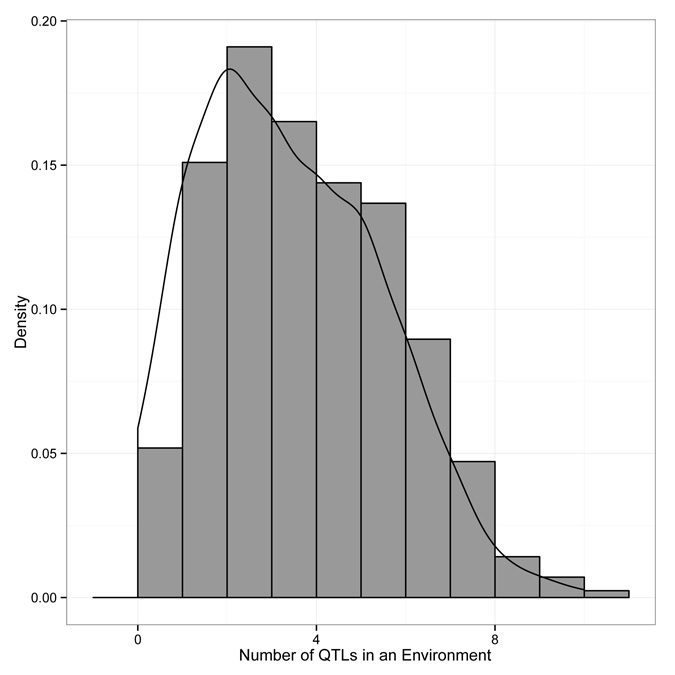
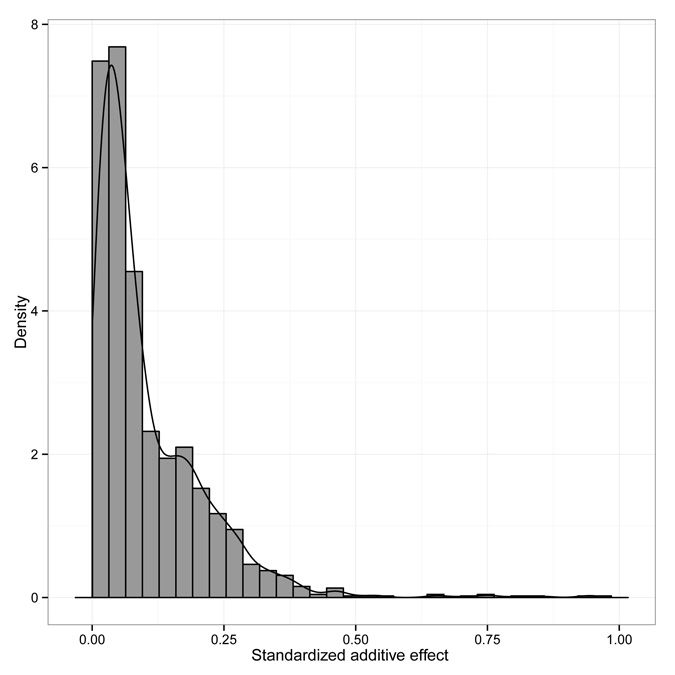
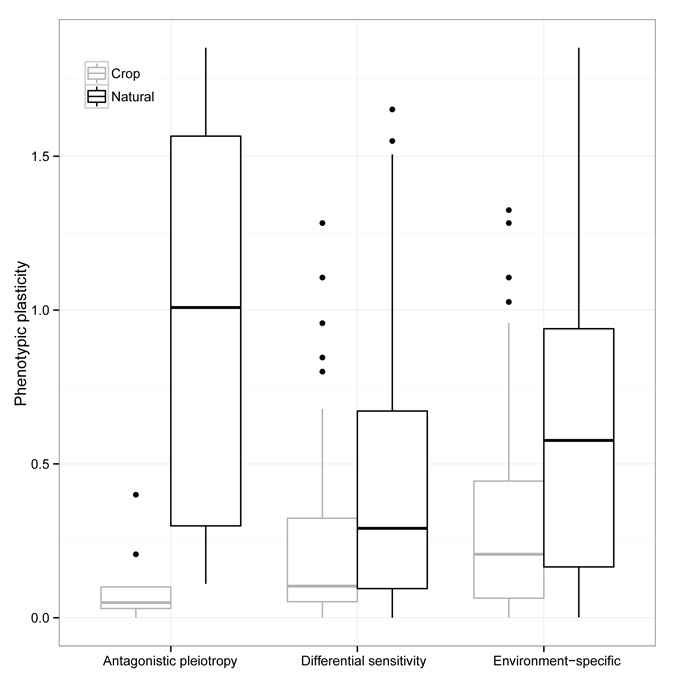
Download the Supplemental Material (PDF). Includes Supplemental Text, Supplemental Figures 1-3 (also reproduced below), and Supplemental Tables 1, 3, and 4. Download Supplemental Table 2 (XLS) Download Supplemental Table 5 (XLS) Supplemental Figure 1: The distribution of the number of QTL for a trait in an environment. Supplemental Figure 2: The distribution of the absolute standardized additive effects across all factors. Supplemental Figure 3: The interaction between genetic architecture and species classes in phenotypic plasticity.