Full text loading...
Methane is the most abundant hydrocarbon in the atmosphere, and it is an important greenhouse gas, which has so far contributed an estimated 20% of postindustrial global warming. A great deal of biogeochemical research has focused on the causes and effects of the variation in global fluxes of methane throughout earth's history, but the underlying microbial processes and their key agents remain poorly understood. This is a disturbing knowledge gap because 85% of the annual global methane production and about 60% of its consumption are based on microbial processes. Only three key functional groups of microorganisms of limited diversity regulate the fluxes of methane on earth, namely the aerobic methanotrophic bacteria, the methanogenic archaea, and their close relatives, the anaerobic methanotrophic archaea (ANME). The ANME represent special lines of descent within the Euryarchaeota and appear to gain energy exclusively from the anaerobic oxidation of methane (AOM), with sulfate as the final electron acceptor according to the net reaction:
This review summarizes what is known and unknown about AOM on earth and its key catalysts, the ANME clades and their bacterial partners.

Article metrics loading...

Full text loading...


Data & Media loading...
Supplemental Material
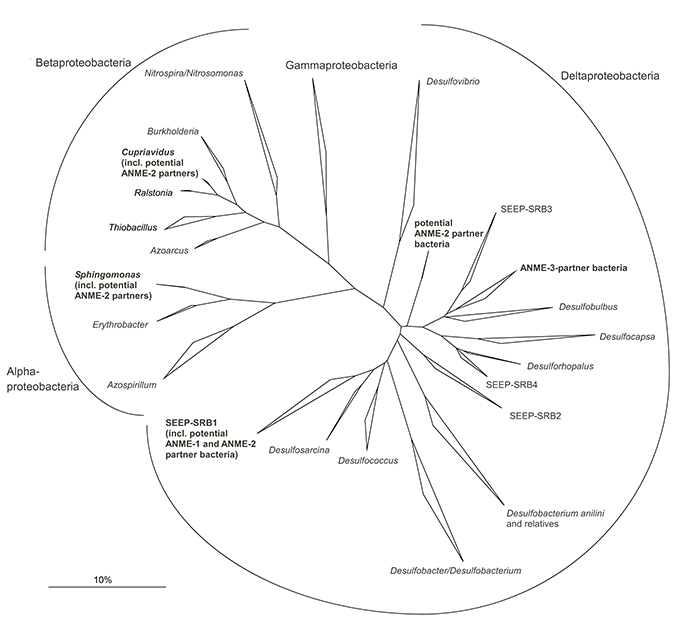
Download all Supplemental Material as a PDF. Includes: Supplemental Figure 1: Phylogenetic tree showing the affiliations of 16S rRNA gene sequences of ANME partner bacteria to selected reference sequences. Desulfosarcina relatives, most likely of the SEEP-SRB1 cluster, and Desulfobulbus relatives have been repeatedly shown to be associated with ANME-1/ ANME-2 and ANME-3, respectively. Recently, Cupriavidus spp. (Betaproteobacteria), relatives of Sphingomonas spp. (Alphaproteobacteria) and another group of the Desulfobulbaceae have been found to live in aggregation with ANME-2 (Pernthaler et al., 2008. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105: 7052-7). Bar, 10% estimated sequence divergence. Supplemental Movie 1.Download video file (AVI) Supplemental Movie 2.Download video file (AVI) Supplemental Movie 3.Download video file (AVI)