Full text loading...
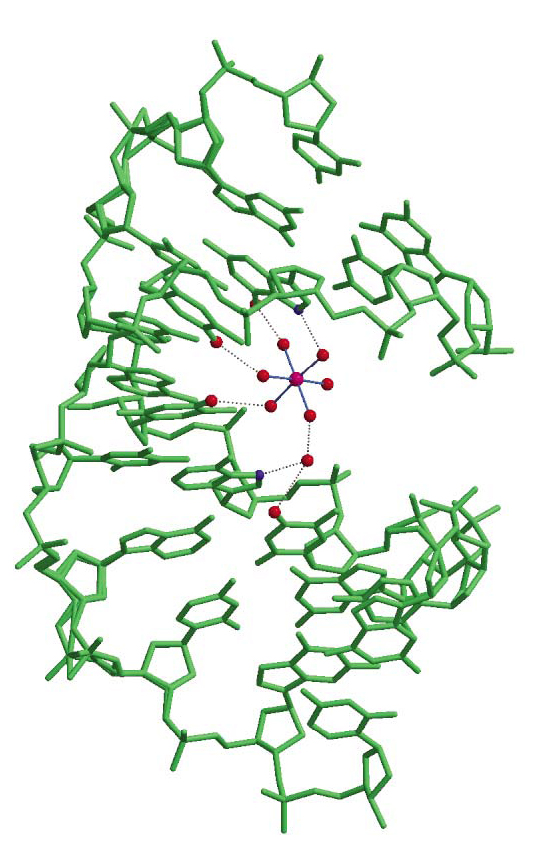
Cations are bound to nucleic acids in a solvated state. High-resolution X-ray diffraction studies of oligonucleotides provide a detailed view of Mg2+, and occasionally other ions bound to DNA. In a survey of several such structures, certain general observations emerge. First, cations bind preferentially to the guanine base in the major groove or to phosphate group oxygen atoms. Second, cations interact with DNA most frequently via water molecules in their primary solvation shell, direct ion-DNA contacts being only rarely observed. Thus, the solvated ions should be viewed as hydrogen bond donors in addition to point charges. Finally, ion interaction sites are readily exchangeable: The same site may be occupied by any ion, including spermine, as well as by a water molecule.

Article metrics loading...

Full text loading...


Data & Media loading...
Supplemental Material
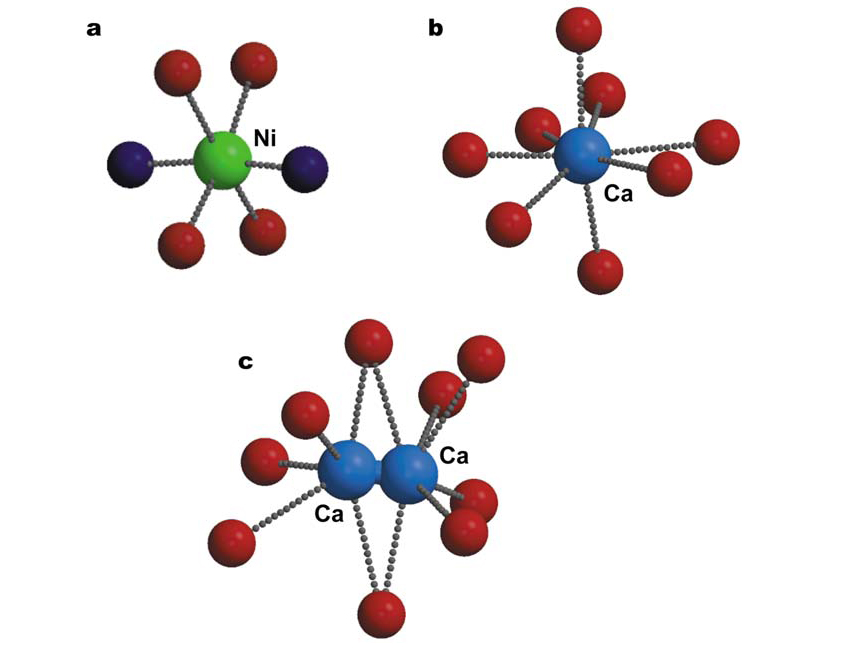
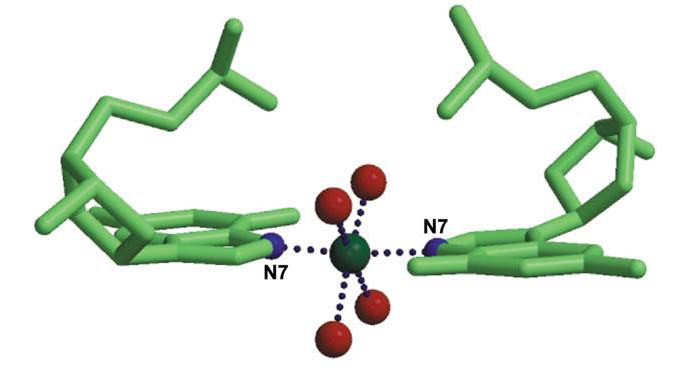
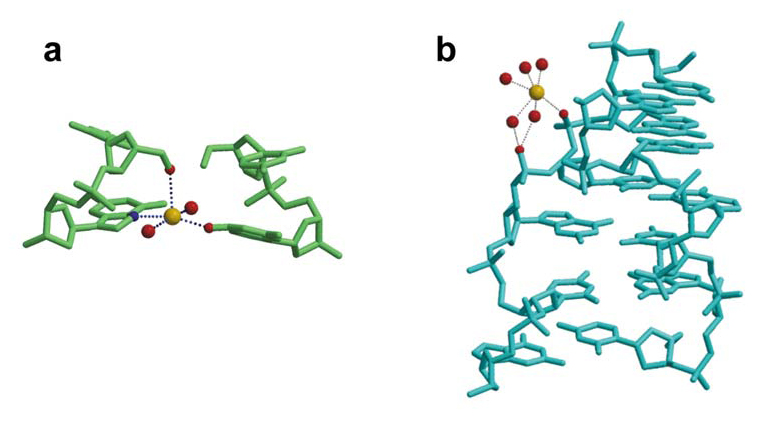
Because most oligonucleotide crystals have been obtained from solutions containing Mg2+ and spermine, relatively little is known about the detailed structure of other divalent cations bound to DNA. Nevertheless, the few available structures indicate that such cations behave similarly to Mg2+. Four examples are briefly considered in Cations as Hydrogen Bond Donors: A View of Electrostatic Interactions in DNA with five additional views of the interaction of solvated ions with DNA pictured below. Download all Supplemental Figures as a single PDF. Figures also reproduced below. Supplemental Figure 8s. Interactions of a solvated Mg2+ ion in A form DNA (AD0007). Waters in the first solvation shell interact directly with three bases on the major groove and with another two bases through a water molecule of the secondary solvation shell. Supplemental Figure 9s. Magnesium as a glue. In most cases magnesium ions stabilize the crystal structure by binding together different duplexes. Three duplexes bound by a single Mg2+ ion (Nr 38) in BD0037 (not shown), five different Mg2+ ions are all involved in stabilizing the crystal. Due to the crystal symmetry, every duplex is in contact with thirteen Mg2+ ions (44). Supplemental Figure 10s. The primary solvation shell of different ions: (a) Ni2+ (1); (b) and (c) Ca2+ (35). In the latter two cases the solvation shell is irregular. In (c) it has been modelled as two Ca2+ ions with partial occupancy. Supplemental Figure 11s. A typical guanine N7 - ion - N7 guanine bridge found in the crystal structure of an oligonucleotide crystallized in the presense of Ni2+ (1). A similar bridge may be formed by Co2+ (78). Supplemental Figure 12s. Examples of two Na+ ions clearly localized in crystals obtained with a low degree of hydration: left, dCpG (10); right, Z-DNA (48). The parallel DNA dimer crystal (10) only contains 3.5 water molecules/base pair and the Z-DNA crystal about fifteen water molecules/base pair (48). Thus these structures are significantly more dehydrated than standard A or B DNA, which contain about twenty five water molecules/base pair. In the case of dCpG, the sodium ion has an additional oxygen from cytosine lying below the square pyramidal face at a long 362 pm distance. It is not clear whether this cystosine atom should be considered part of the solvation layer of Na+. This ambiquity is a further example of the variable solvation of monovalent ions in general.Description