Full text loading...
It is becoming increasingly clear that a large repertoire of noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) are actively transcribed from the mammalian genome, regulating diverse cellular processes in development and diseases through a variety of gene regulatory mechanisms. As the most extensively studied ncRNA species, microRNAs (miRNAs) are important components in the oncogene and tumor suppressor network, and have been employed as potential biomarkers, therapeutic reagents, and therapeutic targets for cancer treatment. Other ncRNAs, particularly long noncoding RNAs, also have a profound impact on cancer development, as demonstrated in both mouse and human tumor models. We are only starting to understand the realm of ncRNA biology, and the exact molecular mechanisms governing ncRNA functions remain largely unexplored. With numerous ncRNAs discovered through high-throughput approaches, understanding their functions in malignant transformation will be one of the most exciting challenges in cancer research.

Article metrics loading...

Full text loading...
Literature Cited


Data & Media loading...
Supplemental Material
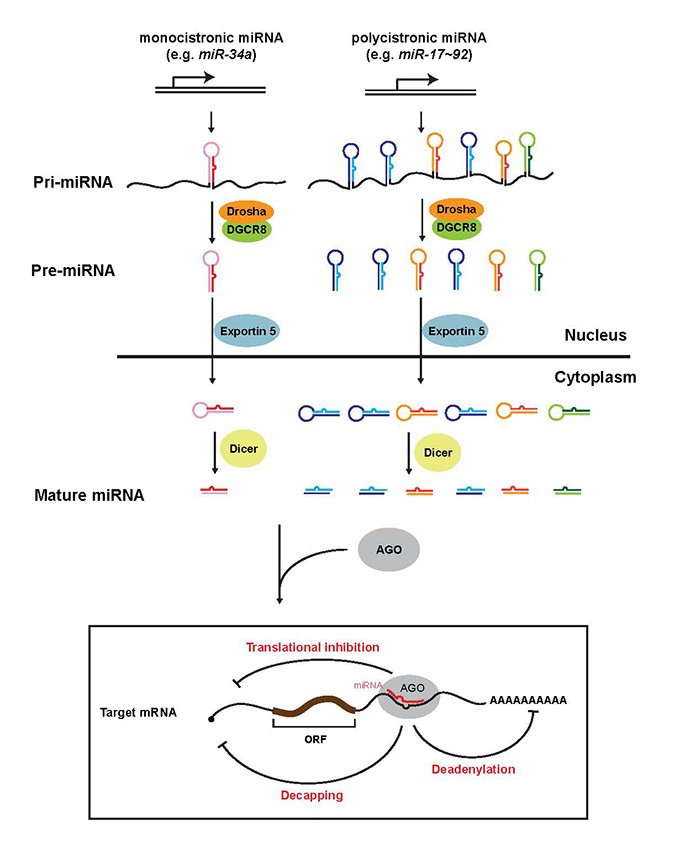
Download all Supplemental Materials as a single PDF. Supplemental Figure 1.The current model for miRNA biogenesis and its post-transcriptional regulation of mRNA targets. Nascent monocistronic or polyscitronic primary miRNAs (pri-miRNAs) are first processed into ~70 nucleotides precursor miRNAs (pre-miRNAs) in the nucleus by the Drosha/DGCR8 microprocessor. Polycistronic pri-miRNAs could contain a tandem of homologous or non-homologous miRNA components. Pre-miRNAs are transported to the cytoplasm by Exportin 5, and subsequently processed into mature miRNA duplexes by Dicer. Only one strand of the miRNA duplex is preferentially incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), and subsequently represses its mRNA targets by mRNA degradation (decapping and/or deadenylation) and/or translational inhibition. The recognition of the mRNA targets by miRNAs requires complementarity between the miRNA seed region (green base pairs) and its targets. ORF, open reading frame. Closed circle, 5’ cap.
Includes Supplemental Figure 1 (also reproduced below), Supplemental Table 1, and Supplemental Literatures.